Steel Manufacturing
Summary
At steel mills, a complex set of processes are employed to convert iron ore, carbon, and trace amounts of other metals into the various grades of steel products. Water is used in almost all of the processes and in most cases a wastewater stream is generated. The wastewater that is generated during these processes can generally be categorized into three sub groups:
- Wet Air Pollution Control (WAPC) Wastewater
- Direct Contact Wastewater
- Machinery cooling and cooling water
Water Uses and Wastewater Sources
Below is a table based off the EPA's Iron and Steel Effluent Guidelines Development Document that provides a brief overview of the water uses and wastewater sources at each stage of the steel manufacturing process.
Process |
Water Uses |
Wastewater Sources |
Cokemaking |
|
|
Sintering |
|
|
Ironmaking |
|
|
Steelmaking (BOF) |
|
|
Steelmaking (EAF) |
|
|
Vacuum Degassing |
|
|
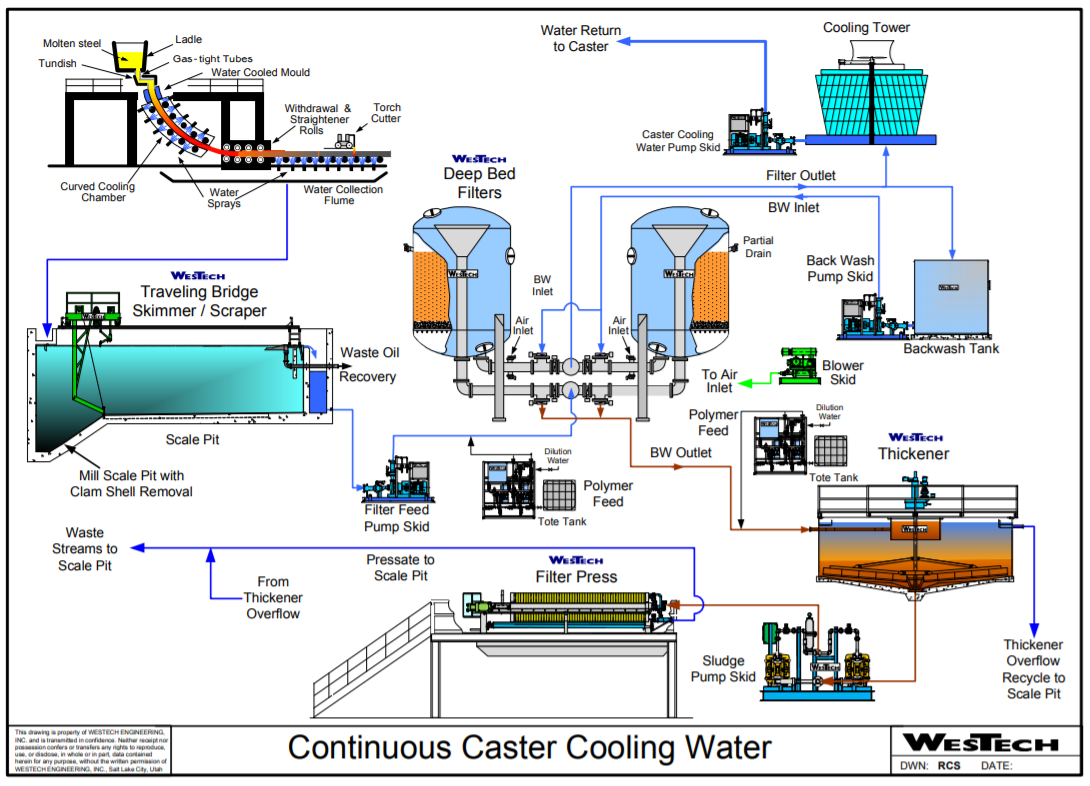
Continuous Casting |
|
|
Hot Forming |
|
|
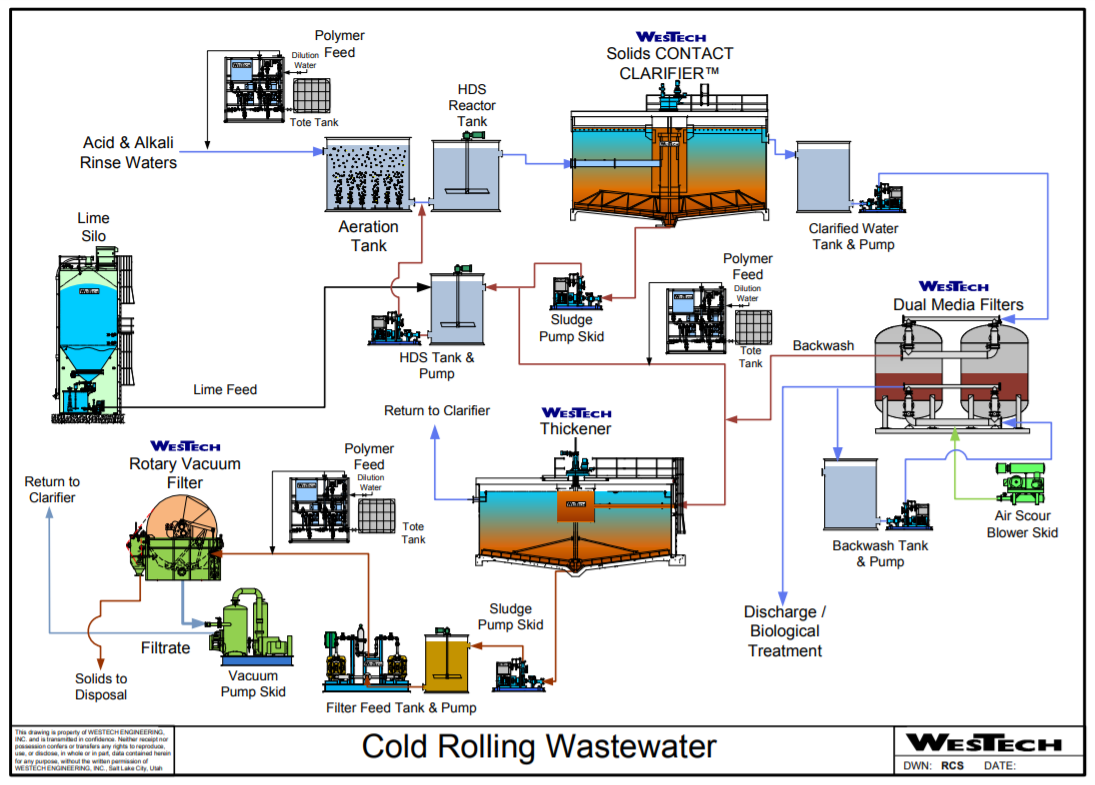
Acid Pickling |
|
|
Alkaline Cleaning |
|
|
Hot Coating / Electropating |
|
|
Process Steps
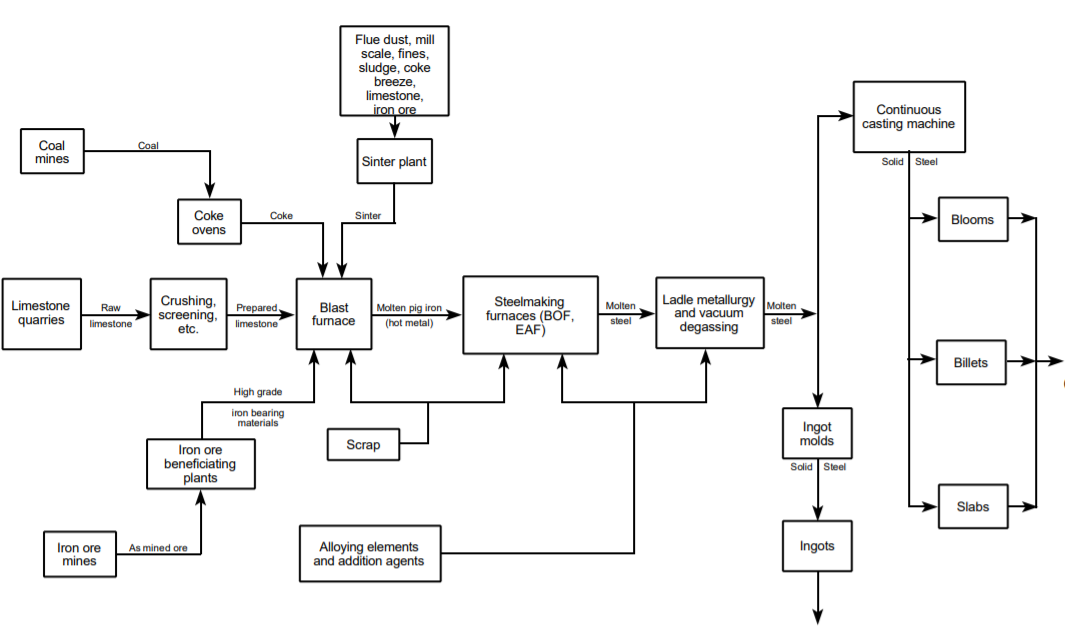
Cokemaking - Turns carbon in raw coal into metallurgical coke which is used in the ironmaking process.
Sintering - Recovers iron from a mixture of mill waste streams and upgrades them to suitable size and weight for the blast furnace.
Ironmaking - Blast furnaces are used to produce molten iron from a mixture of coke, limestone, refined iron ores and sinter.
Steelmaking
Continuous Casting - Molten steel is poured, cooled and formed into a desired shape.
Sintering - Recovers iron from a mixture of mill waste streams and upgrades them to suitable size and weight for the blast furnace.
Ironmaking - Blast furnaces are used to produce molten iron from a mixture of coke, limestone, refined iron ores and sinter.
Steelmaking
- Basic Oxygen Furnace - Oxygen and lime are added to the molten iron from the blast furnace to remove phosphorus and sulfur impurities in the form of slag.
- Electric Arc Furnace - Scrap steel, pig iron and alloying elements are melted by passing an electric current through the furnace. Limestone slag removes steel impurities like sulfur and phosphorus.
Continuous Casting - Molten steel is poured, cooled and formed into a desired shape.
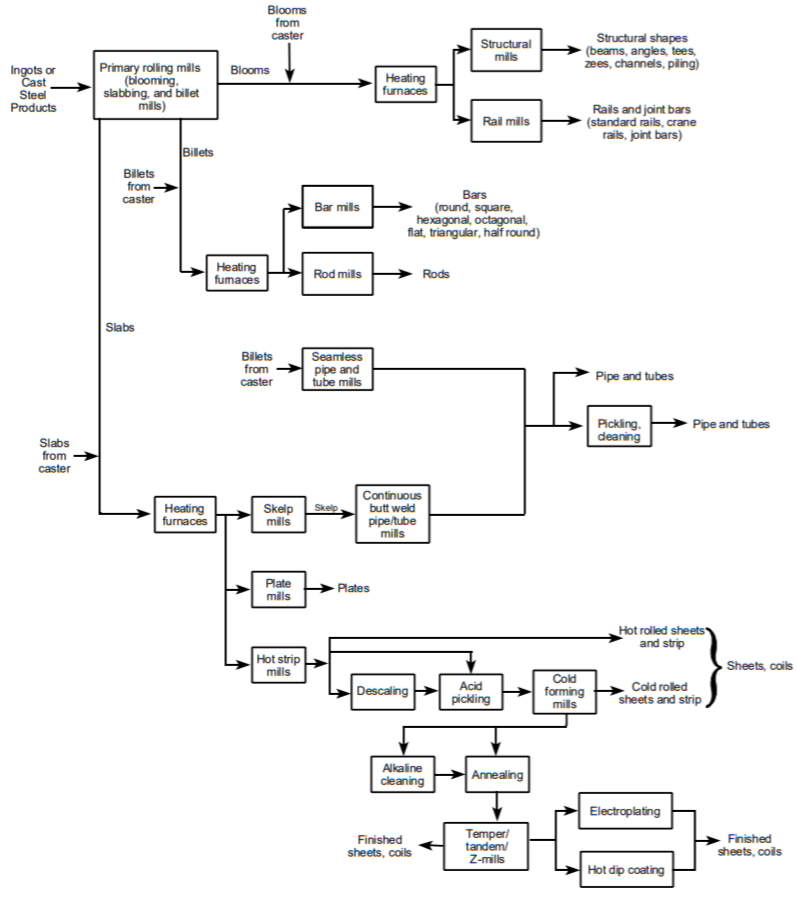
Hot Forming - Preheated solidified steel is reshaped through a series of forming steps in which mechanical pressure is applied through work rolls.
Descaling - Molten salt baths or abrasive compounds are used to loosen and remove heavy scale from stainless and high alloy steels.
Acid Pickling - Chemically removes oxides and scale from the surface of steel using inorganic acid solutions.
Cold Forming - Steel is rolled at ambient temperature to impart desired mechanical and surface properties like hardness, surface finishes and thickness.
Alkaline Cleaning - Steel is passed through alkaline solutions to remove mineral and animal fats and oils.
Hot Coating - Precleaned steel is immersed into molten baths of metals to improve the resistance to corrosion or appearance.
Descaling - Molten salt baths or abrasive compounds are used to loosen and remove heavy scale from stainless and high alloy steels.
Acid Pickling - Chemically removes oxides and scale from the surface of steel using inorganic acid solutions.
Cold Forming - Steel is rolled at ambient temperature to impart desired mechanical and surface properties like hardness, surface finishes and thickness.
Alkaline Cleaning - Steel is passed through alkaline solutions to remove mineral and animal fats and oils.
Hot Coating - Precleaned steel is immersed into molten baths of metals to improve the resistance to corrosion or appearance.
Example Treatment Processes
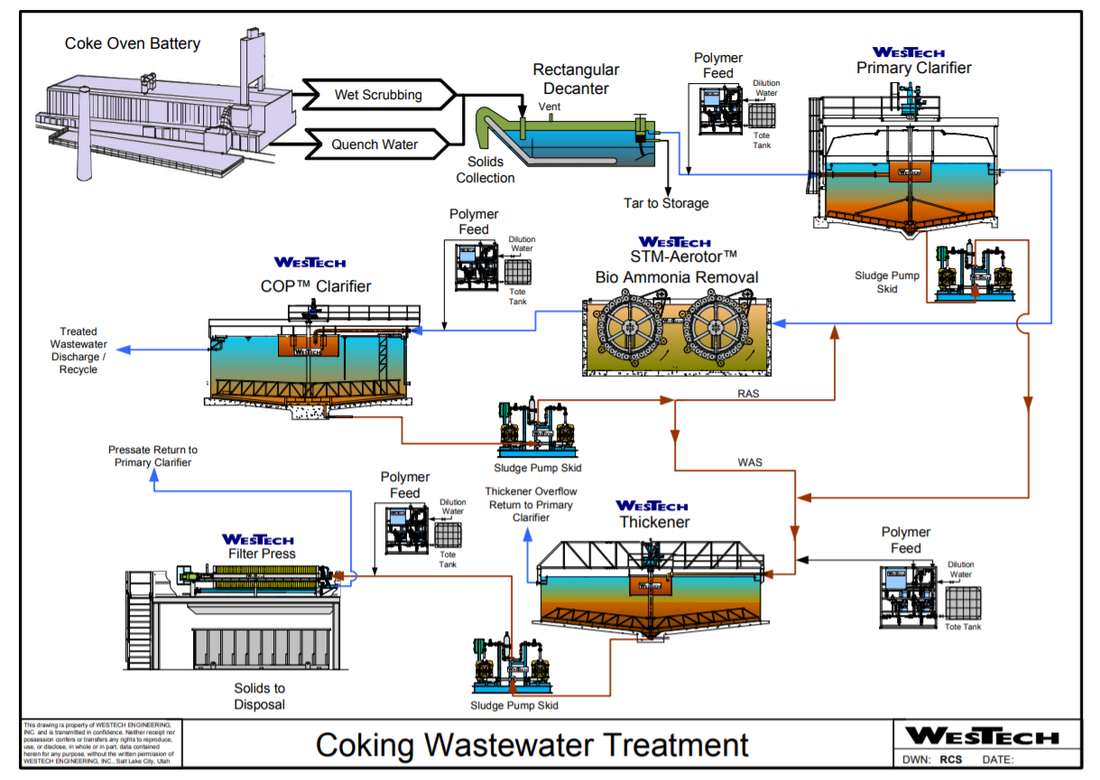
Wastewater from the coke making process is some of the more difficult wastewater to treat at integrated steel mills.