The Basics:
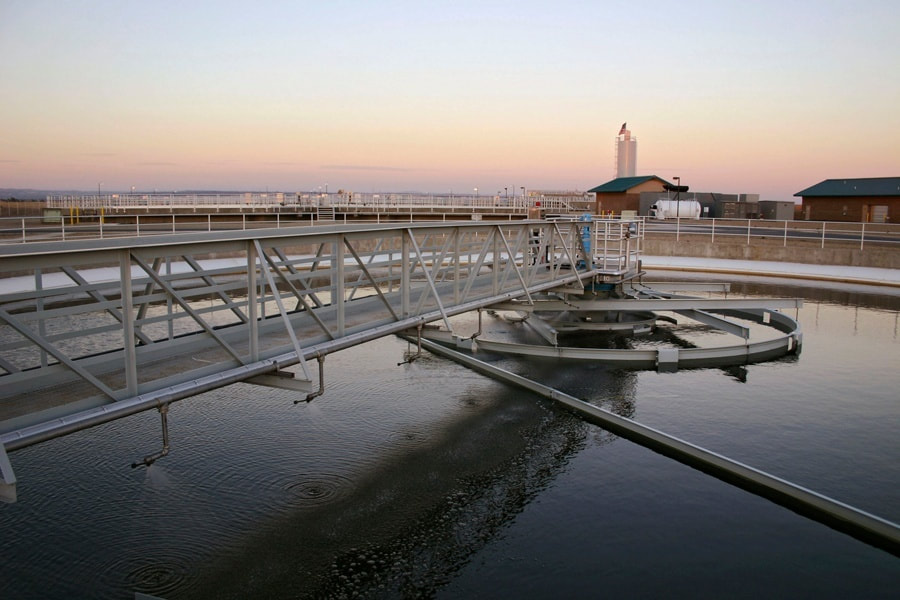
Clarifiers, through gravity sedimentation of a dilute suspension, are used to produce a relatively clear overflow stream. This is in contrast to thickeners which are used to increase the percent solids of the underflow.
Clarifiers are a critical part of many industrial water and wastewater treatment systems. Dilute suspensions of solids in water are generated by a variety of industrial processes. In most cases the solids concentration of the water needs to be reduced before it can be discharged to a municipality or body of water. Clarifiers offer a simple yet effective option to meet these requirements.
Clarifiers are a critical part of many industrial water and wastewater treatment systems. Dilute suspensions of solids in water are generated by a variety of industrial processes. In most cases the solids concentration of the water needs to be reduced before it can be discharged to a municipality or body of water. Clarifiers offer a simple yet effective option to meet these requirements.
In general clarifiers consist of a number of key components:
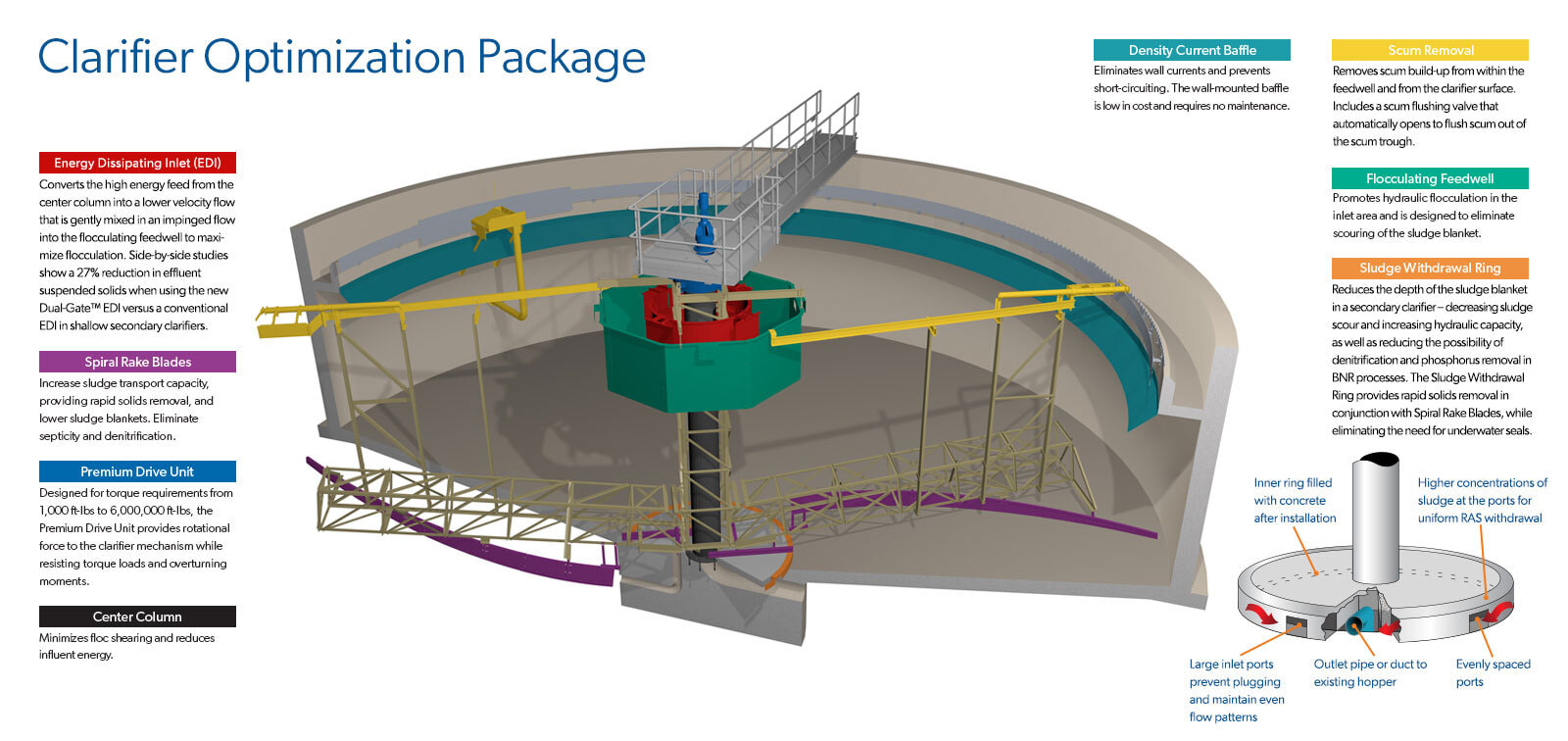
- Inlet System: Typically the dilute suspension is transfered to the clarifier at relatively high energy. This high energy feed needs ot be converted to low velocity flow that is directed downward. This low velocity downward flow allows for effective settling and prevents short circuiting or entrainment of the solids into the clarified effluent. The inlet systems also help promote flocculation of particles to improve settling characteristics and reduce the size of the clarifier significantly.
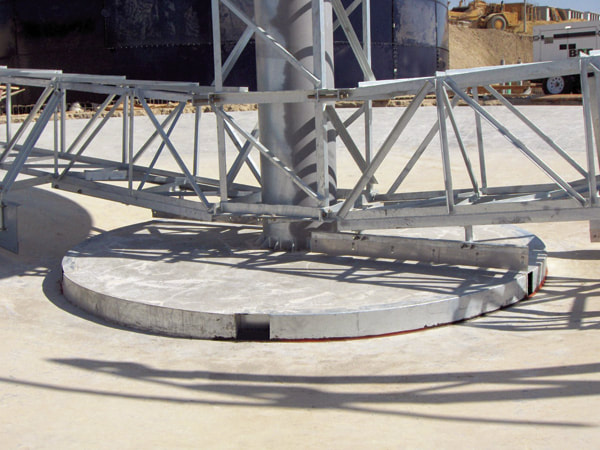
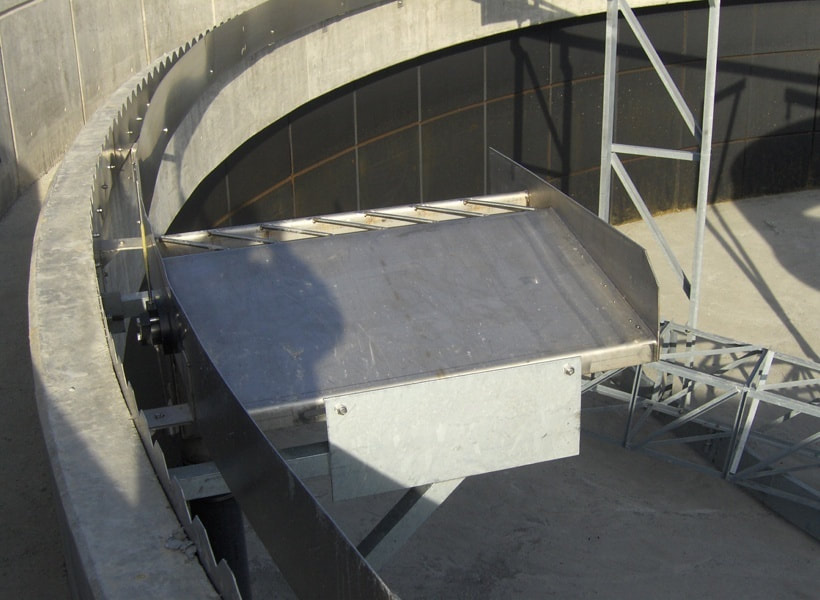
- Sludge Handling: Most clarifiers utilize a mechanical device to gently move the settled solids towards the sludge removal system. Depending on the style of clarifier these mechanisms can take on many shapes and sizes. As the mechanism rotates through the sludge it also helps thicken the sludge and increase it's solids content.
- Scum Removal: The most critical process consideration when designing a sedimentaiton system is how well the solids will settle. With that being said some clarifiers are designed with skimming systems to remove floating material (commonly oily solids or filamentatous bacteria) by pushing it into a trough located at the water surface.
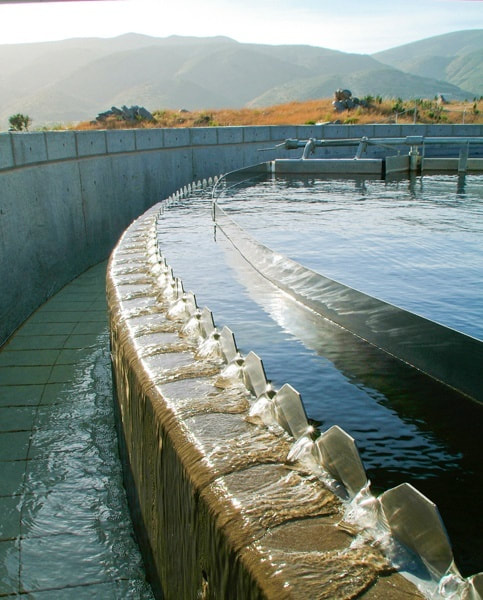
- Clarified Effluent: In order to minimize solids carryover the effluent system is carefully designed and installed to allow the clarified water to exit in an consistent manner.
Variation and Selection
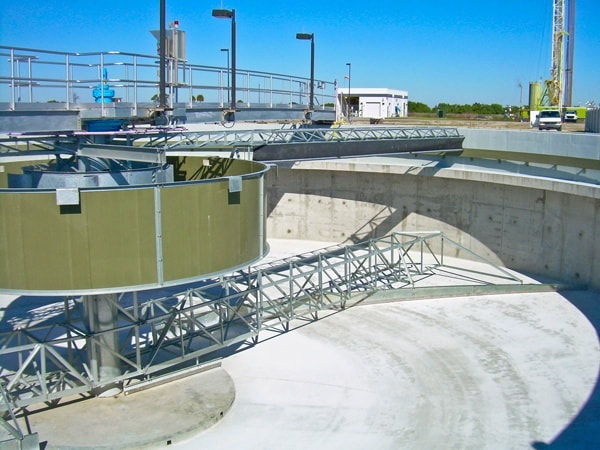
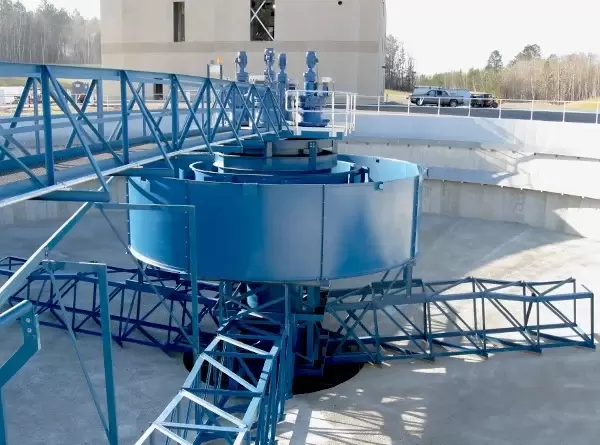
Circular Clarifier: The open style circular clarifier can accommodate a wide range of operating conditions. Because this style clarifier does not have a great deal of internal surfaces it is well suited for biologically active wastewater and wastewater that is subject to variations in solids loading.
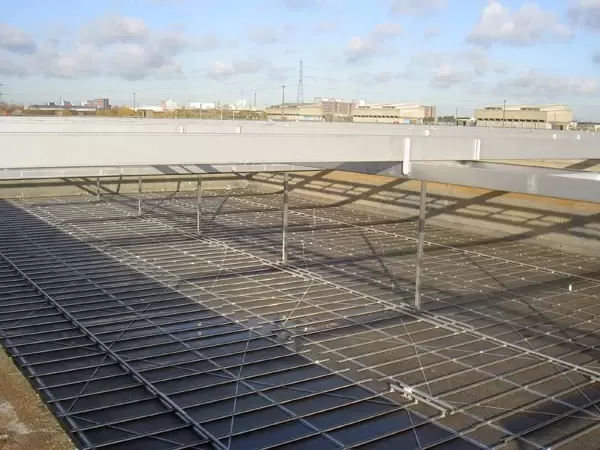
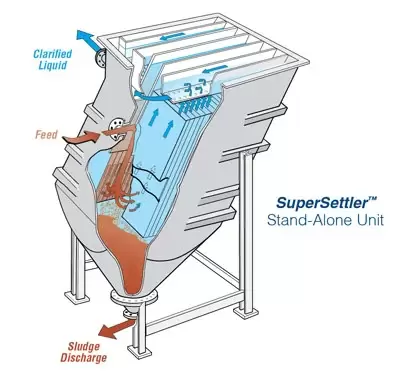
Inclined Plate Clarifier: The addition of parallel plate packs or tube settlers to a clarification system can significantly improve the settling rate of a clarifier. This increased efficiency reduces the footprint required at a given flow rate. Because submerged media is used to improve settling performance, special consideration needs to be given when dealing with biologically active wastewaters or streams that have varying solids loading.
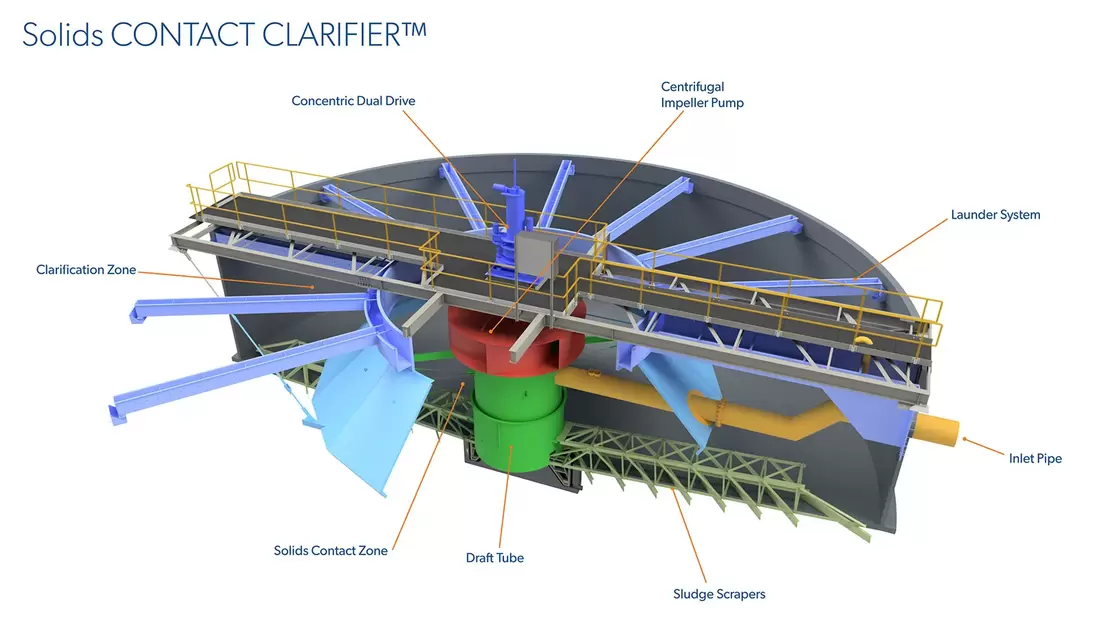
Solids Contact Clarifier: In order to improve flocculation and/or chemical reaction performance it is sometimes beneficial to return some of the settled sludge to the inlet. This improvement occurs because when sludge is recycled with the incoming particles there is a much higher likelihood of interaction occurring which ensures large flocculated particles are formed and chemical reagents are fully utilized. Sludge recycling can take be done external to the clarifier however it is far more efficient to utilize a high flow, low shear impeller inside the clarifier to draw settled sludge back up into the inlet system. Because the amount of solids being recycled is many orders of magnitude higher than what is contained in the incoming wastewater, Solids Contact Clarifiers are very effective with dilute suspensions or suspensions that are prone to high variation.
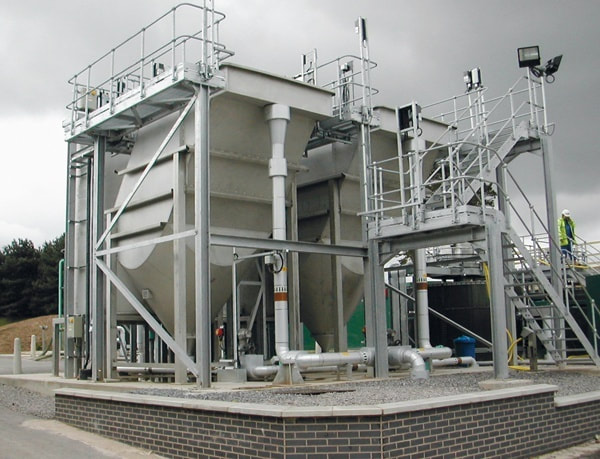
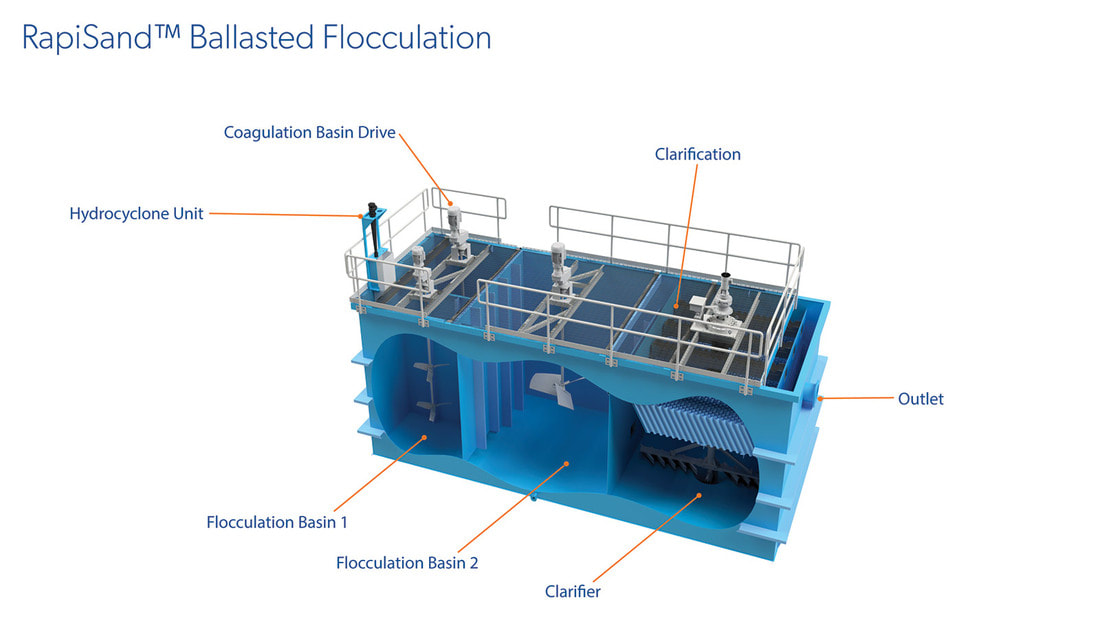
Ballasted Flocculation Clarifiers: When solids do not settle rapidly or foot print is limited weighting agents can be added to improve settling characteristics. These types of clarifiers typically employ a weighting agent addition and recovery systems. In some cases the foot print reduction can be significant.